🛳️Kubernetes
Provision a Kubernetes cluster
First you'll need a Kubernetes cluster. If you have one already you can skip and directly go to the Onyxia instalation section.
Hashicorp maintains great tutorials for terraforming Kubernetes clusters on AWS, GCP or Azure.
Pick one of the three and follow the guide.
You can stop after the configure kubectl section.
Ingress controller
Let's install ingress-ngnix on our newly created cluster:
DNS
Let's assume you own the domain name my-domain.net, for the rest of the guide you should replace my-domain.net by a domain you actually own.
Now you need to get the external address of your cluster, run the command
and write down the External IP assigned to the LoadBalancer.
Depending on the cloud provider you are using it can be an IPv4, an IPv6 or a domain. On AWS for example, it will be a domain like xxx.elb.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com.
If you see <pending>, wait a few seconds and try again.
Once you have the address, create the following DNS records:
If the address you got was an IPv4 (x.x.x.x), create a A record instead of a CNAME.
If the address you got was ans IPv6 (y:y:y:y:y:y:y:y), create a AAAA record.
https://datalab.my-domain.net will be the URL for your instance of Onyxia. The URL of the services created by Onyxia are going to look like: https://<something>.lab.my-domain.net
SSL
In this section we will obtain a TLS certificate issued by LetsEncrypt using the certbot commend line tool then get our ingress controller to use it.
If you are already familiar with certbot you're probably used to run it on a remote host via SSH. In this case you are expected to run it on your own machine, we'll use the DNS chalenge instead of the HTTP chalenge.
Now we want to create a Kubernetes secret containing our newly obtained certificate:
Lastly, we want to tell our ingress controller to use this TLS certificate, to do so run:
This command will open your configured text editor, go to containers -> args and add:
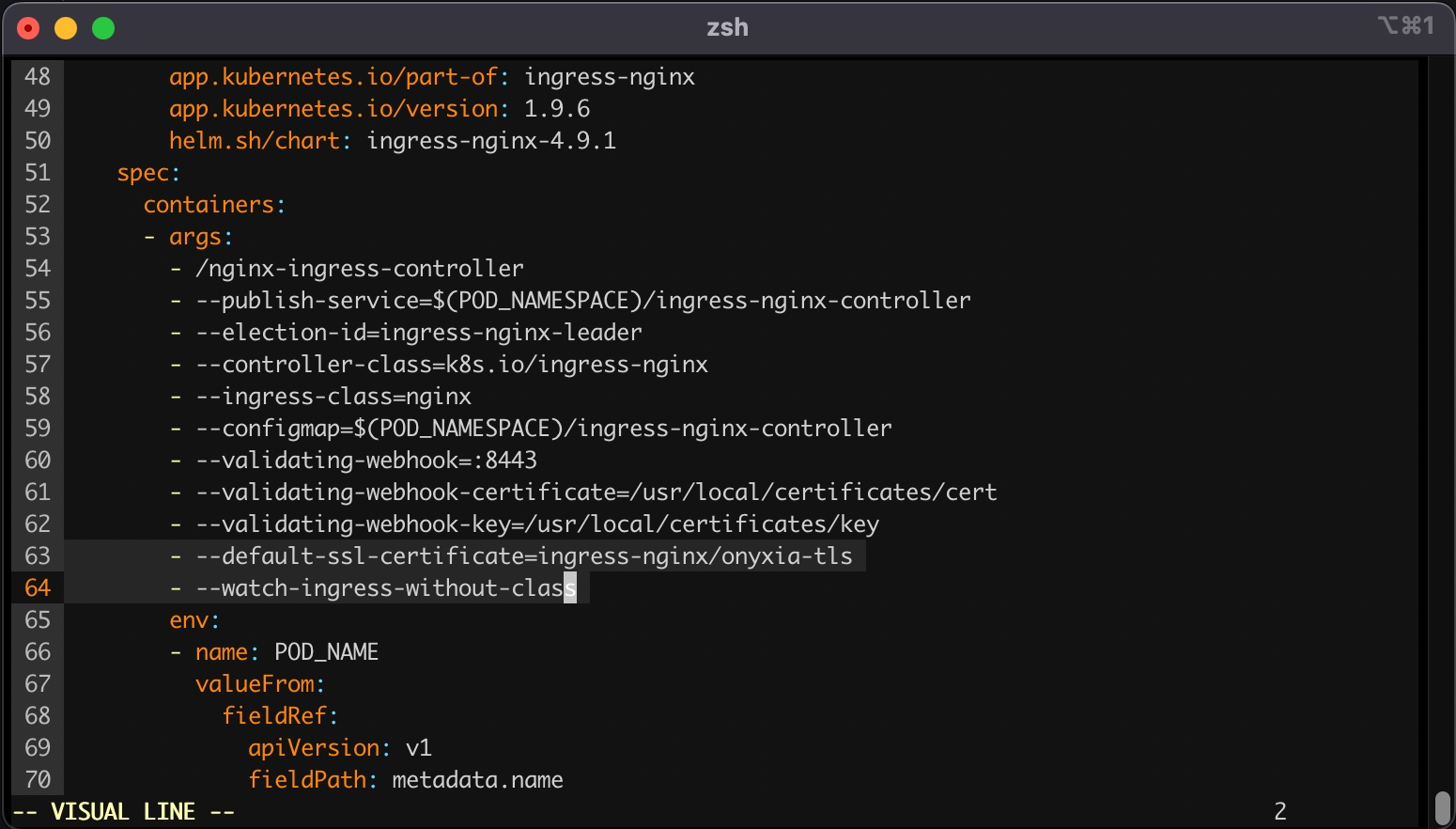
Save and quit. Done 🎉 We installed the ingress-nginx in our cluster, (but note that any other ingress controller could have been used as well). The configuration was adjusted to handle all ingress objects, even those lacking a specified class, and to employ our SSL certificate for our wildcard certificate. This strategy facilitated an effortless SSL termination, managed by the reverse proxy for both *.lab.my-domain.net and datalab.my-domain.net, thus removing any additional SSL configuration concerns.
If you are on a Mac or Window computer you can install Docker desktop then enable Kubernetes.
WARNING: If you are folowing this installating guide on an Apple Sillicon Mac, be aware that many of the services that comes by default with Onyxia like Jupyter RStudio and VSCode won't run because we do not yet compile our datacience stack for the ARM64 architecture. If you would like to see this change please sumit an issue about it.
Port Forwarding
You'll need to forward the TCP ports 80 and 443 to your local machine. It's done from the administration panel of your domestic internet Box. If you're on a corporate network you'll have to test onyxia on a remote Kubernetes cluster.
DNS
Let's assume you own the domain name my-domain.net, for the rest of the guide you should replace my-domain.net by a domain you actually own.
Get your internet box routable IP and create the following DNS records:
If you have DDNS domain you can create CNAME instead example:
https://datalab.my-domain.net will be the URL for your instance of Onyxia.
The URL of the services created by Onyxia are going to look like: https://xxx.lab.my-domain.net
SSL
In this section we will obtain a TLS certificate issued by LetsEncrypt using the certbot commend line tool.
Now we want to create a Kubernetes secret containing our newly obtained certificate:
Ingress controller
We will install ingress-nginx in our cluster, although any other ingress controller would be suitable as well. The configuration will be set up to handle all ingress objects, including those without a specified class, and to utilize our SSL certificate for our wildcard certificate. This approach ensures a straightforward SSL termination managed by the reverse proxy for both *.lab.my-domain.net and datalab.my-domain.net, eliminating any further concerns regarding SSL setup.
Now that we have a Kubernetes cluster ready to use let's levrage ArgoCD and GitOps practices to deploy and monitor the core services of our Onyxia Datalab.
🐙GitOpsLast updated
Was this helpful?